Wyniki wyszukiwania
39 results for query Data
Reports(8)
-
How to ensure that the consumer improves the security of the energy system and benefits from it?

Ordinary Kowalski can improve the security of the energy system and at the same time save money. It is enough to change the energy tariffs and provide up-to-date information on how much electricity we use. In winter, the power system can be offloaded by 200MW. The annual costs of households could fall by as much as 160 PLN.
1.2.2017 -
Electricity and industrial competitiveness

Industrial competitiveness is at the centre of the Polish debate about the future (and the logic) of climate and energy policy. There is a widely held opinion that low prices are the most important condition for a thriving industry.
19.12.2014 -
Energy transition in Poland | Edition 2019

Growing imports of gas, coal and electricity. Increasing importance of gas in the energy mix and stagnation in RES. Increase in greenhouse gas emissions. These are the most important conclusions from this year's edition of the report "Energy Transition in Poland" prepared by the Forum Energii. Full report in English will be available soon.
9.4.2019 -
Heating in Poland | 2019 edition

While the battle for new climate targets for 2050 is under way in Brussels, many Polish cities and villages are already struggling with smog. Forum Energii gathered the most important data on heating in order to highlight the importance of heating, which is treated as a poor cousin of the energy sector.
16.12.2019 -
Energy transition in Poland | 2020 Edition

Electricity production from coal is decreasing, electricity imports are increasing; the importance of gas in the energy mix continues to grow, and renewable energy sources also play a more important role in the system. These are the key conclusions of the Forum's recent study "Energy transition in Poland". This is the third edition of the report, which presents key data on the state of the Polish energy sector and its changes.
11.3.2020 -
Energy transition in Poland | 2021 Edition

The production of electricity from coal in Poland is decreasing. For the first time in the country’s history, in 2020 coal’s share in the generation mix dropped below 70%. Renewable sources have slowly started to play a more important role in the mix, as well as gas. In the midst of the pandemic, domestic production has fallen faster than demand, and this gap is filled by energy imports. Poland remains the most expensive electricity market in the region.
17.3.2021 -
Energy transition in Poland | 2022 Edition

On top of the economic slowdown in 2020 caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, 2021 was the next year when the cards dealt unexpected circumstances that diverged from the previous years of stability. In Europe, we experienced an energy crisis marked by sharp spikes in gas prices and CO2 emission costs. The wartime reality of 2022 means even more uncertainty and market volatility with energy security and independence from imported raw materials becoming the most important topics. Poland continues drifting along in the modernisation of the energy sector, as clearly indicated by data collected by Forum Energii in its annual report “Energy Transition in Poland”.
25.4.2022 -
Energy transition in Poland | 2023 edition

2022 was another year of unexpected events. Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine changed Europe’s approach to fossil fuel imports, particularly from Russia. The resulting energy crisis triggered by high gas prices and the decline in nuclear and hydroelectric production led to record high energy prices across Europe. These events are changing the way European countries look at the energy transition. Meanwhile, the modernisation of the Polish energy sector is still very slow. An overview of the increasingly comprehensive data on the energy sector is published by Forum Energii in the sixth edition of the report ‘Energy Transition in Poland. Edition 2023’.
17.4.2023
Insights(30)
-
Spring is coming in the DSR

Last year, PSE launched the first edition of the DSR program. Its outcomes are positive. However, this year it could be much better. Apart from the second edition of the PSE program, the capacity market is also starting.
5.4.2018 -
Power deficit in the Polish power system in August 2015

The heat wave which affected the whole country from the beginning of August, in combination with the hydrological conditions of the main rivers, resulted in deterioration of the operating conditions of power generation equipment and power networks in Poland. As a result, PSE SA (Polskie Sieci Elektroenergetyczne, the Transmission System Operator) imposed various levels of limitations of power supply for industrial consumers until the end of August. Such measures were taken for the first time in many years.
23.9.2015 -
A low-emission economy is a global model

The Paris Agreement is not only a success for the negotiators, but above all evidence of the growing interest in the development of a low-emission economy. According to the International Energy Agency, within 5 years RES capacity will constitute 60% of all power in the energy sector. Despite the fact that we are only talking about capacities and the real production of green energy is lower, it is a strong signal concerning the trend of energy production in the world.
16.11.2016 -
Capacity market auction results | What next?

On November 15, 2018 PSE S.A. (state owned transmission system operator in Poland) held the first auction as part of the new scheme of remunerating capacity, that is a capacity market. The auction secured 22.7 GW for 2021 for a total amount of over 5 billion PLN (over 1,2 billion EUR). The cost of the capacity scheme appears significantly higher than the 4 billion the Ministry of Energy assumed for the year.
19.11.2018 -
Poland’s Energy and Climate Plan to 2030 – not sufficient EU perspective

The National Energy and Climate Plan 2021-2030 is the second strategic document for the Polish energy sector in addition to the long-awaited Poland’s Energy Policy until 2040. It will affect, among other things, investments in the energy sector, the implementation of our international commitments, energy security and improvement of air quality. Therefore, it should not only describe the current state of the Polish energy sector, but above all define future objectives and determine measures and actions to achieve them.
26.2.2019 -
Draft Poland's Energy Policy 2040 - new and better?

On the 8th of November 2019, the Ministry of Energy has presented an updated draft of Poland's Energy Policy until 2040. Yet, the adoption of the energy strategy will be the responsibility of the new government, including new ministries - the Ministry of State Assets and the Ministry of Climate. In our opinion, it is high time for Poland to address the climate and energy crisis. It is also important for us to start implementing the commitments made at the EU forum. The energy sector should be given a course in line with international trends, and not be allowed to float in a random direction.
29.11.2019 -
2020 RES target: what if Poland does not reach it?

Poland, along several other European Union Member States, is unlikely to meet its national 15% renewable energy target for 2020 on time[1]. However, despite the possibility to impose sanctions for failure to meet national obligations, including financial penalties, the European Commission is not interested in punishing countries just for the sake of punishment. The potential consequences for countries that are lagging behind should be understood rather as a means of mobilising them to catch up, but also to increase their ambitions to meet the second of the EU RES targets - the one set in the 2030 horizon.
17.3.2020 -
Renewables in the Polish energy mix. Still not enough to meet the targets

The energy transformation has accelerated significantly. Thanks to the enormous cost reduction of solar PV and onshore wind, these technologies are increasingly being chosen by the private sector and households as an investment that allows for significant savings. In recent years, however, the development of renewable energy sources (RES) has depended on state policies and support schemes. They were to enable Poland to achieve the so-called RES target - renewables were to account for 15% of gross final energy consumption in 2020[1]. According to our estimates, the target is still far from being achieved - in 2019 the share of RES amounted to 11.5% only and everything indicates that this year too, the result of 15% is out of reach.
23.7.2020 -
Obligation to sell electricity on power exchange―no time for sudden moves
The Ministry of Climate and Environment have announced its plans to abolish the obligation to sell electricity on power exchange by generators, a so-called ‘obligo’. A public consultation on the proposed law is underway. The topic seems technical and niche. But the effects of the planned changes will be widespread: with the electricity market not very competitive, the abolition of the obligation will increase wholesale prices and have a negative impact on consumers―mainly industrial ones. This is a step backwards in terms of competition and transparency of the electricity market in Poland.
24.2.2021 -
The purpose of the EU-ETS and its pending reforms

Since the beginning of the year, CO2 emission allowance prices have risen by 70%, from EUR 30 to over EUR 50 per tonne. The rate of this increase has again triggered discussion in Poland on the purpose of the Emissions Trading System’s (EU-ETS) existence. Meanwhile, the EU discussion on the ETS, which is due to begin shortly, will not be about whether to abolish the system, but how to reform it so that the EU can achieve its decarbonization goals. Carbon pricing will be the most important tool for achieving the EU's 55% emissions reduction target in 2030. In this text, we explain the system’s basic operational principles and highlight expected discussion topics and possible upcoming changes.
2.6.2021 -
Poland needs 2 GW of new photovoltaic capacity annually - that's why prosumers should be supported

The government is announcing changes in the support system for prosumers. The combination of the current operational support scheme (a version net-metering, called “rebates”), subsidies in the form of the “Mój Prąd” program and tax credits resulted in rapid development of solar energy in Poland. Within a few years the installed capacity in micro-installations increased from 200 MW to 3.3 GW. Security of energy supply in the summer has strengthened, CO2 emissions have been reduced and the generation mix has become more diversified to some extent. Citizens have fallen in love with renewables for good. So what’s next?
23.6.2021 -
From 2025 coal will leave the Polish energy system in waves

Poland’s energy sector is entering a period of major turbulence. The immediate question is the continued operation of the Turów power station since the EU Court of Justice recently ordered the suspension of lignite mining there. This is just the beginning of the problems. After 2025, when public support ends, the first 8 GW of coal capacity may leave the Polish system, and a little later, another 6 GW. The power plants will be shut down due to age and costs. Observing the government’s actions, one can get the impression that all hope lies in the proposed National Agency for Energy Security . Yet, this is a side discussion because no change in ownership structure will improve the situation of the failing coal power industry. Instead, difficult decisions must be made, and the possibilities of supporting the operation of coal-fired power plants with public money are already very limited.
27.7.2021 -
The spectre of the ETS gap

In the following months, negotiations on the Fit for 55 package, which was proposed by the European Commission in July this, year will continue. One of the key elements of these negotiations is the reform of the EU Emissions Trading System (EU-ETS). The Polish government is arguing that the number of allowances allocated to Poland will be lower than the emissions of installations covered by the ETS, creating a so-called imbalance of CO2 emission allowances. Where does the imbalance come from, and can it be reduced? And is this the most important element in negotiations of the new EU ETS? We explain below.
27.8.2021 -
E-mobility - a chance for further development of economic cooperation between Poland and Germany

The Polish and German economies work in a system of interconnected vessels.Even if the echoes of the visit of the new German Chancellor Olaf Scholz to Poland suggest that there are many issues that divide us, there are also those that unite us. For instance the development of electromobility may raise this cooperation to a higher level, but it is necessary to prepare strategically for it. The focus should be on cooperation in the area of technological developmentbattery production and recycling, joint planning of infrastructure, as well as exchange and sharing of knowledge, especially in the area of innovation.
20.12.2021 -
The capacity market in Poland―more expensive than ever

Poland has already held six power auctions. Analysis of their results shows that this mechanism in its current form is not an optimum solution for the country. The capacity market has proved more expensive than anticipated, has failed to curb the increase in electricity prices and, in addition, has contributed to the petrification of the outdated and coal-based generation structure. The arduous task of plugging the coal gap has only just begun, which is why decisions on modernisation and on methods for supporting capacity up to 2030 must be taken urgently.
13.1.2022 -
Poland has spent more than a trillion zloty (EUR 220 billion) on fossil fuel imports since 2000

In recent months, rising energy prices have caused panic among policymakers. Gas and coal prices on world markets are at record highs, and crude oil is also becoming more expensive. In addition, Poland has become one of the EU countries most dependent on fossil fuel imports.
18.1.2022 -
Lack of transformation hikes energy prices, not climate policy

A recent information campaign led by energy companies and echoed by politicians, suggests that CO2 accounts for as much as 60% of the electricity cost. This message creates an impression that the cost of buying allowances amounts to 60 percent of the end users’ electricity bill. But this is not the case. It does a great deal of harm - it distracts attention from the fundamental problems of the Polish energy sector. It distances us from solutions that can effectively stop price increases. In this article - on the basis of adopted assumptions (presented in the annex) we present, among others, what energy prices for households are actually made of.
4.2.2022 -
The end of energy resource imports from Russia?

On February 24, Russia started the Ukrainian war. Nothing will be the same again. Russia's brutal attack made the ongoing conflict around energy resources all the more obvious. In 2021 alone Russia could have earned PLN 500 billion (or $120 billion). from the export of energy resources[1]. This revenue funds the Kremlin's military spending. Now we are considering whether giving up Russian fossil fuels is possible. Undoubtedly, this would be a radical solution with far-reaching and not entirely known consequences. If this were to happen, solidarity and close cooperation within the EU would be more important than ever before. In this article, we analyze what options Poland has to break its energy dependence on Russia.
28.2.2022 -
Ukraine's Power System: Peace and War
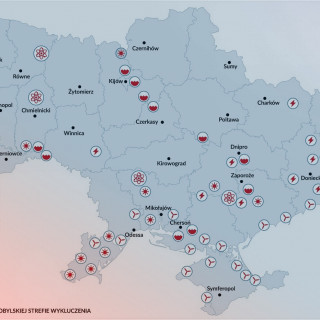
On 16 March, Ukraine was synchronised with the electricity grid of continental Europe, bidding a permanent farewell to the systems of Russia and Belarus. The connection took place in an urgent and emergency procedure. This is an important step towards sustainable cooperation with the European Union. But today, in Ukraine, there is first and foremost a warfare, as well as an energy war, which is no less important for the lives of the civilian population of Ukraine and Europe as a whole.
17.3.2022 -
Is the Kremlin turning off the gas tap? Time to exclude gas and coal from households

How to prepare households for an energy war with Russia? Gazprom is suspending gas supplies to Poland under the Yamal contract. This is no great surprise. At the end of this year, Poland was going to give up buying Russian gas anyway. Physically, there is unlikely to be a shortage of gas, but Poland is entering a period of high prices, which will limit the use of this raw material. The role of the state should be to wisely support society in smoothly passing through the crisis. Without reducing demand in sectors where it is possible, this will be difficult.
28.4.2022 -
Whom to ask how Poland spends billions from the Modernisation Fund?

The European Union has decided to allocate 2% of the allowances from its emissions trading system (EU-ETS) for support to poorer countries in their energy transition. Since 2021 this money is transferred to Poland, among others. The local operator – the National Fund for Environmental Protection and Water Management – has been distributing the funds without adequate public scrutiny and information. A year after taking charge of the Modernisation Fund, there is no transparent website to adequately inform society and potential applicants on what and how over EUR 11 bn (PLN 50 bn) is to be spent (and a further increase is on the table). This article deals with the consequences of the current flaws in this process and why their removal is so important for Poland.
23.5.2022 -
Ukraine’s Preparations for a Wartime Winter

Ukraine has prepared relatively well for the heating season, despite the Russian invasion and subsequent war, which has been ongoing for more than six months. The accumulated stocks of coal and gas are likely to be sufficient to ensure heat and electricity supply. The decline in demand for electric power due to reduced economic activity during the war is greater than the lost generation potential, enabling Ukraine to export electricity to the EU. The biggest challenge will be to secure heating if the Russian shelling of CHP plants intensifies. This could cause a humanitarian catastrophe in Ukraine and increase the number of refugees.
28.9.2022 -
Україна готується до зими в умовах воєнного часу

Україна відносно добре підготувалася до опалювального сезону, незважаючи на російське вторгнення, яке триває вже понад півроку. Накопичених запасів енергетичного вугілля та газу, ймовірно, буде достатньо для належного забезпечення тепло- та електропостачання. При цьому зниження попиту на електроенергію внаслідок відтоку частини населення та скорочення економічної активності під час війни є відчутно більшим, ніж втрачений за час ведення бойових дій та окупації потенціал генерації. Такий «розрив» між поточними попитом та пропозицією на внутрішньому ринку дозволяє Україні експортувати електроенергію до ЄС, тоді як модернізація інфраструктури передачі електроенергії відкриває можливості збільшення обсягів такого експорту. Разом з тим найбільшим викликом буде забезпечення теплопостачання у разі посилення російських обстрілів ТЕЦ та інших значущих об’єктів енергетичної інфраструктури. Це може призвести до гуманітарної катастрофи в Україні та збільшення потоку біженців до країн ЄС.
6.10.2022 -
How to maintain Belchatow's energy future

Europe is going through its biggest energy crisis ever. The attention of decision makers is focused on ensuring energy and heat supplies in the coming months. Meanwhile, long-term challenges and problems in the energy sector that have not been solved before are only accumulating. One of them is the future of the largest power plant in Poland.
15.11.2022 -
Renewables can reduce fuel imports

Last year the import of gas, oil and coal cost Poland PLN 89 billion. This year, it will be much more - by the end of June it already amounted to PLN 85 billion[1]. The supply crunch and spike in fuel prices have become the source of an economic and energy crisis, and a means of exerting pressure on Europe. Meanwhile, renewables not only reduce emissions and energy prices, but also import dependency on energy resources.
29.11.2022 -
Conclusions from the 7th capacity market auction - cleaner, but adequacy remains a challenge

The results of the seventh auction in the Polish capacity market clearly show the dilemma Poland has faced - existing high-carbon (coal) capacity can no longer be supported with this mechanism, while gas is risky due to the geopolitical situation. Although Polish energy companies have not completely abandoned gas projects, fewer appeared in the auction than previously announced. There is also clearly a greater variety of technologies than before - for the first time, contracts were granted to storage. The market is still expensive - for the second year in a row auctions ended in the first round and at the maximum price.
20.1.2023 -
Russian oil disappearing from Europe

In 2021, about a quarter of the oil used in the EU, about €48 billion worth in total, came from Russia. The invasion of Ukraine prompted EU countries to impose sanctions on this commodity. However, the sanctions contain loopholes that have made Poland the EU’s largest importer of Russian oil. While sealing the sanctions regime is possible, electrification of transportation will in the long run safeguard against the risk of replacing dependence on Russia with dependence on other petrostates.
9.2.2023 -
Billions of Euros for LNG and LPG still flowing from the EU to Russia

The EU embargo on Russian fuels did not extend to natural gas (including LNG, liquefied natural gas) or LPG (liquefied petroleum gas). In 2022 alone, EU countries paid as much as 16 billion euros for Russian LNG, a record high. Poland did not import any LNG from Russia, however it is the largest importer of LPG in the entire EU. In 2022, Poland spent about 700 million euros on Russian LPG. In this article, Forum Energii will explain how to close the loopholes in the EU embargo on Russian resources to finally eliminate them from the EU market.
29.3.2023 -
Europe needs a new energy security strategy

The European Union’s Energy Security Strategy was adopted in 2014, shortly after Russia’s annexation of Crimea. By now, not all of it has been implemented, and some of its points are outdated. After ten years and Russia’s full-scale attack on Ukraine—and in the era of a climate crisis—the EU’s energy security strategy needs to be rewritten. The basis of this strategy should be a cost-effective, but also decentralized, digitalized and decarbonized energy system based on renewable sources in which energy efficiency plays the key role. Such a future is worth fighting for.
28.7.2023 -
Anatomy of Dependence: How to Eliminate Rosatom from Europe

EU countries depend on cooperation with Russia in the field of nuclear energy. This has meant that even despite the Russian full-scale invasion of Ukraine, the Rosatom corporation has not been sanctioned and trade in this sector is growing. This situation is unfavourable for the EU and increases its vulnerability to blackmail from Russia. Moreover, it strengthens the Russian military. The EU should increase its efforts to diversify supplies and build its own capabilities in the nuclear sector.
5.9.2023
Events(1)
-
Forum Energii LIVE – webinar series
26.3–22.6.2020
The coronavirus pandemic is keeping us at home. Let's use this time to meet on the Internet. We have prepared a series of webinars: Forum Energii LIVE. We present the most important data on the energy sector, energy transformation and heating sector, but also we discuss the challenges and opportunities that the global economic crisis presents to Governments and the energy industry.